What Are the Symptoms of Fibroids?
While many women with uterine fibroids experience no symptoms at all, approximately 50% of women with fibroids do end up having symptoms. Fibroids symptoms can vary from mild to extremely severe and depend on the number of fibroids you have, as well as their location and size.
What are the most common symptoms of fibroids?
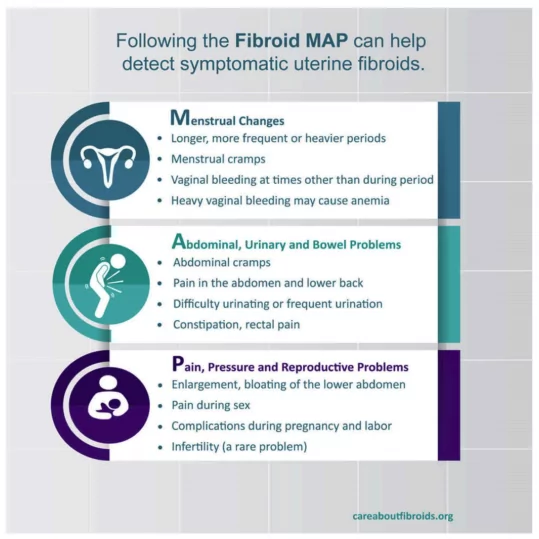
Need help deciphering your symptoms? Check out this Fibroid MAP by CARE About Fibroids.
Heavy and/or extended menstrual bleeding
Fibroids connected to your uterine lining can cause pressure that makes your endometrial tissue bleed more than usual. Endometrial tissue is what grows in the uterus to prepare the womb lining for ovulation. Even small fibroids located within the lining of the uterine wall can cause excessive bleeding.
Pelvic pressure or pain
The size, weight, placement, and quantity of your fibroids can pull, stretch, push, and place undue compression or strain on the inside and outside of the uterus—as well as the surrounding organs—resulting in pelvic pressure or pain.
Interference with sexual intercourse
Fibroids can cause painful sexual intercourse, although this typically only occurs in specific positions or at certain angles. They can also lower your sex drive by altering your estrogen and progesterone hormone levels.

Are you suffering from pain and discomfort without knowing the source?
It may be time to get checked for uterine fibroids.
(This image is by @katemangostar on Freepik.)
Weight gain and stomach bulge
Your uterus is approximately the size of a pear. While some fibroids are only the size of a pea, others, if left untreated, can grow to be the size of mangos, cantaloupes, or watermelons. Even a medium-sized fibroid can create a stomach bulge that mimics pregnancy.
Frequent urination or urinary incontinence
Fibroids can push on the bladder—creating a sense of needing to urinate frequently and sometimes interfering with bladder control. The size and placement of your fibroids may make urination painful, too.
Constipation
Fibroids may exert pressure on your bowels, causing constipation and/or uncomfortable elimination.
Lower back and leg pain
Depending on location, a medium to large fibroid may press on the pelvic nerve—sending pain to your lower back, butt, hip, or thigh. Pressure on the sciatic nerve may send shooting pains down the back of your leg.
Learn more about Uterine Fibroids
Stay informed with the latest news and developments delivered right to your personalized newsfeed in Responsum for Fibroids
What are the most common symptoms of fibroids?
If you have fibroids and are pregnant, there are some potential complications that could occur—the most common of which is pain.
(This image is by @serhii_bobyk for Freepik.)
Complications during pregnancy or labor
As stated by the American Society of Reproductive Medicine, “Fibroids are found in 2% to 12% of pregnant women, but not all fibroids get larger or cause problems in pregnancy. If a fibroid grows, it usually does so in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.”
The potential complications for pregnant women with fibroids include the following:
- Fetal growth restriction: The size of fibroids may prevent a fetus from growing to its full capacity due to less room in the womb.
- Placental abruption: This is when the placenta breaks away from the uterine wall because a fibroid is blocking the way.
- Pre-term delivery: Fibroids-related pain may lead to contractions, which can result in early delivery.
- Cesarean delivery (C-section): Women with fibroids are six times more likely to deliver via C-section.
- Baby in breech position: Fibroids may change the shape of the cavity, which may not allow the baby to align properly for a vaginal delivery.
- Miscarriage: Women with fibroids’ chances of miscarrying double in comparison to women without fibroids.
Difficulty conceiving and/or infertility
Fibroids can interfere with conception in a number of different ways, such as whether:
- Sperm and egg meet
- An embryo can implant
- A pregnancy can continue
On rare occasions, fibroids can cause infertility. Fibroid location and size are what affect fertility, such as submucosal fibroids (inside the uterine cavity) or large (over 6 cm in diameter) intramural fibroids (in the uterine wall).
What should I do if I think I have symptoms?
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your doctor or medical provider to determine if you have fibroids. If you are diagnosed with fibroids, you and your doctor will determine a treatment plan to help alleviate your fibroids symptoms and improve your quality of life, including physical, mental, and emotional health.

